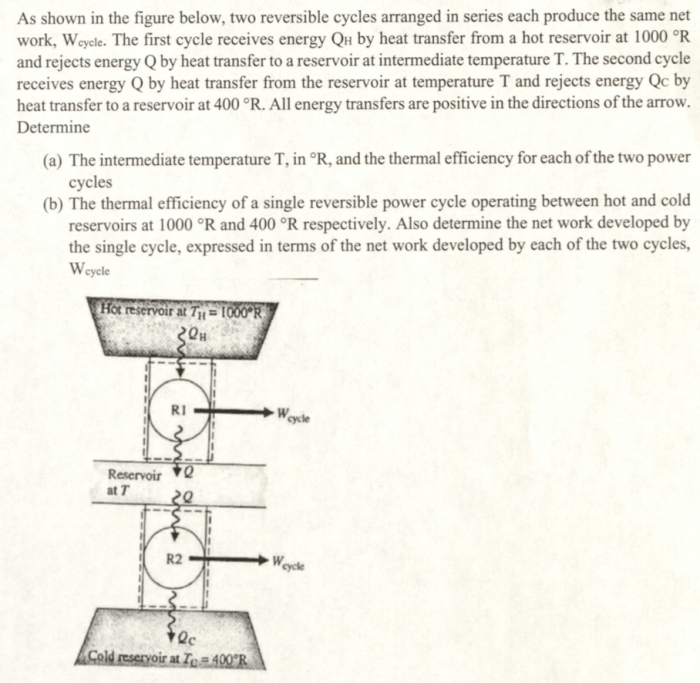
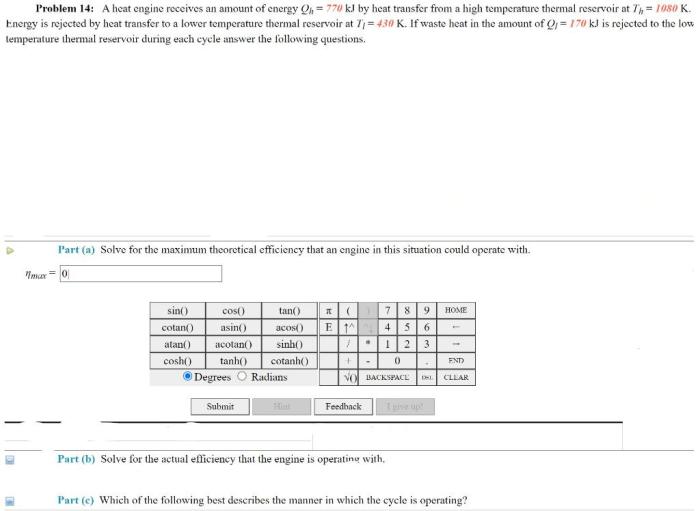
How much heat Qh is rejected to the room is a crucial consideration in various engineering applications. This comprehensive analysis delves into the fundamental concepts of heat transfer, exploring the mechanisms and factors that influence heat rejection. By understanding these principles, engineers can optimize system efficiency and achieve desired thermal performance.
Heat rejection plays a vital role in maintaining the thermal balance of systems, ensuring their proper operation. This analysis provides a detailed examination of the methods used to calculate heat rejection, considering the assumptions and limitations of each approach.
Heat Transfer Fundamentals
Heat transfer is the movement of thermal energy from one object or region to another. It occurs in three primary modes: conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conductionis the transfer of heat through direct contact between two objects. For example, when you touch a hot stove, heat from the stove is transferred to your hand through conduction.
Convectionis the transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid (liquid or gas). For example, when you boil water, heat from the bottom of the pot is transferred to the water through convection currents.
Radiationis the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. For example, heat from the sun is transferred to the Earth through radiation.
The rate of heat transfer is influenced by several factors, including the temperature difference between the objects, the surface area of the objects, the material properties of the objects, and the presence of any intervening medium.
Heat Rejection to the Room
Heat rejection refers to the transfer of heat from a system to the surrounding environment. It is an important aspect of system efficiency, as it affects the overall performance and energy consumption of the system.
Heat rejection can occur through the same modes as heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. For example, a computer generates heat during operation, which is rejected to the room through conduction through the computer case, convection through the air flow generated by the fans, and radiation from the surfaces of the computer.
Systems that reject heat to the room include HVAC systems, power plants, and electronic devices.
Calculating Heat Rejection
The amount of heat rejected to the room can be calculated using various methods, including:
- Experimental methods:Involves measuring the temperature difference between the system and the room, as well as the heat flow rate.
- Analytical methods:Uses mathematical equations and models to calculate the heat rejection based on system parameters and operating conditions.
- Numerical methods:Employs computational techniques, such as finite element analysis, to solve complex heat transfer problems and determine the heat rejection.
The accuracy and applicability of these methods depend on the specific system and the available information.
Factors Affecting Heat Rejection
Several factors affect the amount of heat rejected to the room, including:
- System operating conditions:The heat rejection rate is directly proportional to the system’s power consumption and operating temperature.
- System design:The physical design of the system, including the surface area, materials, and cooling mechanisms, influences the heat rejection rate.
- Environmental conditions:The temperature and humidity of the surrounding environment can affect the rate of heat rejection.
- Heat transfer mechanisms:The relative contribution of conduction, convection, and radiation to the overall heat rejection depends on the system and environmental conditions.
Applications of Heat Rejection, How much heat qh is rejected to the room
Heat rejection is an essential aspect of various applications, including:
- HVAC systems:Heat rejection is used to remove excess heat from buildings, maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature.
- Power plants:Heat rejection is necessary to dissipate the waste heat generated during power generation, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient operation.
- Electronic devices:Heat rejection is crucial for preventing overheating and maintaining the performance and reliability of electronic devices.
Optimizing heat rejection can improve system efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and extend the lifespan of equipment.
Popular Questions: How Much Heat Qh Is Rejected To The Room
What is the significance of heat rejection in engineering systems?
Heat rejection is crucial for maintaining thermal equilibrium and ensuring proper system operation. By removing excess heat, systems can operate within their designed temperature range, preventing overheating and potential damage.
How can heat rejection be optimized in practical applications?
Optimizing heat rejection involves considering factors such as heat transfer surface area, fluid flow rates, and thermal conductivity of materials. By carefully selecting and designing these parameters, engineers can enhance heat dissipation and improve system efficiency.