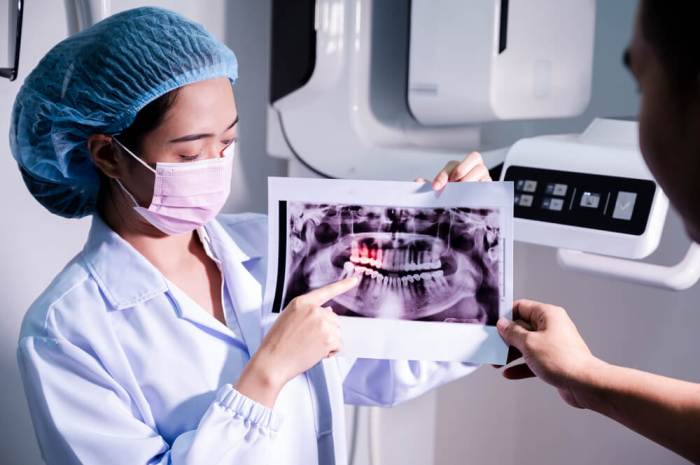
Positioning instruments in digital radiography: play a pivotal role in ensuring accurate and reliable images. This article delves into the types, applications, and importance of these instruments, exploring their impact on patient positioning, image quality, radiation safety, and advanced techniques.
Proper positioning of patients is crucial for optimal image acquisition. By understanding the principles and practices of positioning instruments, radiographers can effectively minimize radiation exposure, enhance image quality, and improve patient care.
Positioning Instruments in Digital Radiography: Positioning Instruments In Digital Radiography:
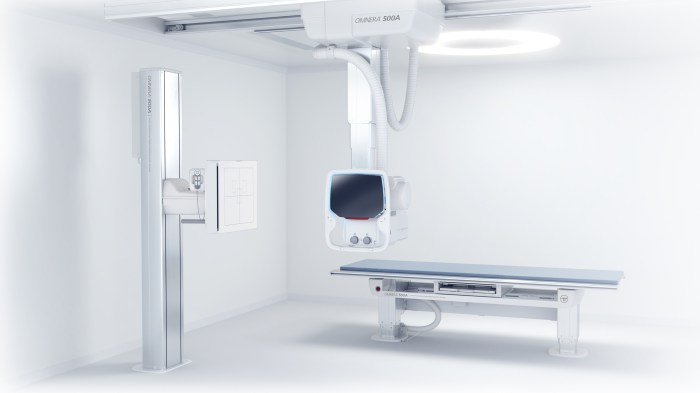
Positioning instruments play a crucial role in digital radiography by ensuring accurate and reliable images. Proper patient positioning is essential for minimizing artifacts, reducing radiation exposure, and optimizing image quality.
Equipment and Techniques
- Positioning grids: Align the patient perpendicular to the X-ray beam, ensuring consistent image density.
- Radiolucent table: Allows for patient positioning and manipulation during examinations.
- Patient supports: Immobilize and support patients, such as headrests, armrests, and leg rests.
- Cassettes and imaging plates: Hold the X-ray film or detector in the correct position.
Specific examples include:
- Chest X-rays: Use a positioning grid to align the patient’s chest to the X-ray beam.
- Abdominal X-rays: Use a radiolucent table to position the patient supine or prone.
- Extremity X-rays: Use patient supports to immobilize and align the affected extremity.
Patient Positioning
Guidelines for patient positioning include:
- Correct anatomical alignment
- Minimal patient movement
- Adequate exposure of the target area
- Positioning aids (sandbags, wedges)
| Examination | Positioning |
|---|---|
| Chest | Supine or upright, PA or AP projection |
| Abdomen | Supine or prone, centered over the target area |
| Extremities | Aligned with the X-ray beam, immobilized with supports |
Image Quality, Positioning instruments in digital radiography:
Proper positioning directly impacts image quality by:
- Minimizing artifacts (e.g., motion blur, geometric distortion)
- Ensuring optimal image density and contrast
- Reducing the need for retakes due to poor positioning
Positioning errors can lead to:
- Incorrect anatomy visualization
- Missed or obscured lesions
- Increased radiation exposure
Standardized positioning protocols ensure consistency and accuracy.
Radiation Safety
Proper positioning can minimize radiation exposure by:
- Correctly aligning the target area to the X-ray beam
- Minimizing scatter radiation by using lead shielding
- Positioning the patient as close as possible to the detector
Safe positioning practices include:
- Using lead shielding to protect patients and staff
- Minimizing the number of retakes
- Following radiation safety guidelines
Advanced Techniques
Advanced positioning techniques include:
- Tomosynthesis: Creates a series of cross-sectional images, reducing superimposition.
- Fluoroscopy: Real-time imaging for dynamic examinations, such as swallowing studies.
- Computer-aided positioning systems: Automated positioning using computer software, reducing examination time and improving accuracy.
Detailed FAQs
What are the different types of positioning instruments used in digital radiography?
Positioning instruments include grids, cassettes, and immobilization devices such as sandbags, wedges, and straps.
How does proper positioning affect image quality?
Incorrect positioning can lead to artifacts, distortion, and poor image quality, affecting diagnostic accuracy.
What are the guidelines for positioning patients for various anatomical regions?
Guidelines vary depending on the region being imaged. For example, chest radiographs require the patient to stand upright with arms raised, while abdominal radiographs require the patient to lie supine with the abdomen compressed.
How can advanced positioning techniques improve patient positioning?
Advanced techniques such as tomosynthesis and fluoroscopy allow for more precise and detailed images, reducing the need for repositioning and minimizing radiation exposure.