Select all correct descriptions of peptidyl transferase. – Peptidyl transferase, a key enzyme in protein synthesis, plays a crucial role in the elongation stage of translation. Its structure, mechanism of action, and regulation are essential for understanding the intricate processes of protein synthesis.
Delving into the complexities of peptidyl transferase, this comprehensive overview explores its structural components, elaborates on its detailed mechanism of action, and discusses the factors that influence its regulation. Additionally, it highlights the clinical significance of peptidyl transferase, showcasing its role in diseases and potential therapeutic applications.
Definition of Peptidyl Transferase
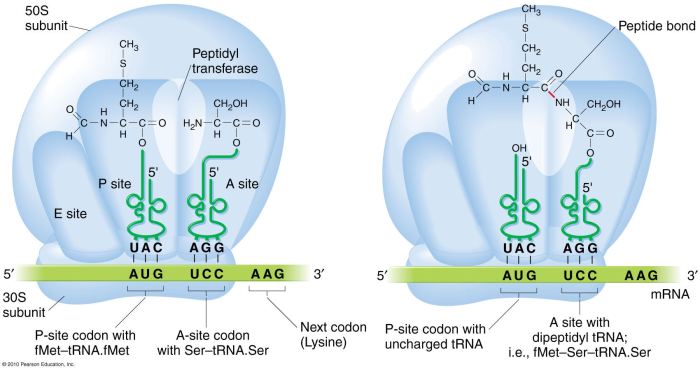
Peptidyl transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds during protein synthesis. It is responsible for joining amino acids together to form the polypeptide chain that constitutes a protein.
Structure of Peptidyl Transferase: Select All Correct Descriptions Of Peptidyl Transferase.
Peptidyl transferase is a large, multi-subunit enzyme that is located in the large subunit of the ribosome. It consists of two main subunits: the catalytic subunit and the tRNA-binding subunit. The catalytic subunit contains the active site where the peptide bond is formed, while the tRNA-binding subunit binds the tRNA molecules that carry the amino acids.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of peptidyl transferase involves the following steps:
- The tRNA molecule that carries the growing polypeptide chain binds to the A site of the ribosome.
- The tRNA molecule that carries the next amino acid binds to the P site of the ribosome.
- The catalytic subunit of peptidyl transferase catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between the amino acid on the P site tRNA and the amino acid on the A site tRNA.
- The tRNA molecule that was on the P site is released from the ribosome.
- The tRNA molecule that is now on the A site moves to the P site.
- The tRNA molecule that carries the next amino acid binds to the A site of the ribosome.
Role in Translation
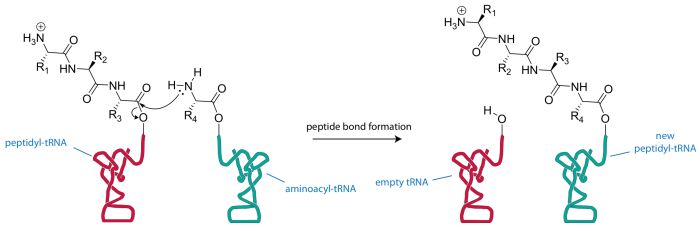
Peptidyl transferase plays a crucial role in protein translation. It is responsible for joining the amino acids together to form the polypeptide chain that constitutes a protein. Without peptidyl transferase, protein synthesis would not be possible.
Regulation of Peptidyl Transferase
The activity of peptidyl transferase is regulated by a number of factors, including:
- The concentration of amino acids in the cell
- The presence of antibiotics
- The temperature
- The pH
Clinical Significance
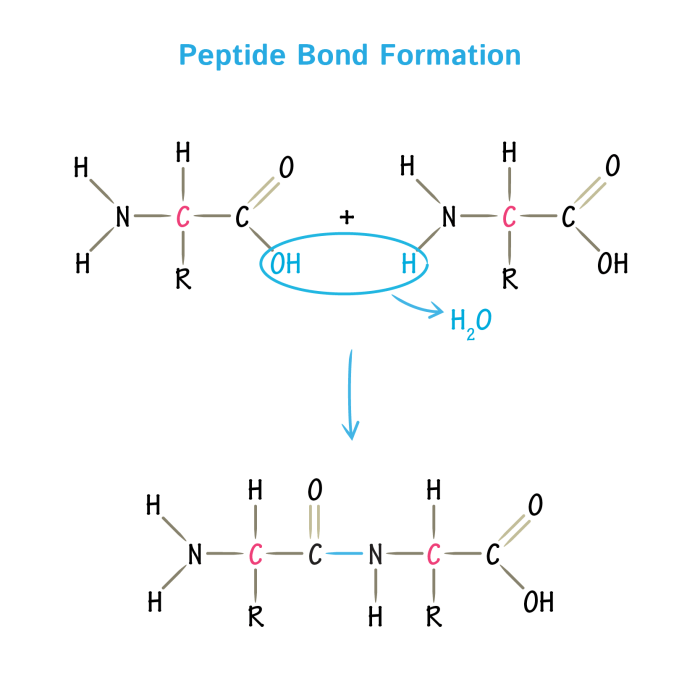
Peptidyl transferase is a potential target for antibiotics. Antibiotics that inhibit peptidyl transferase can prevent the synthesis of proteins, which can lead to the death of the bacteria.
Examples of Peptidyl Transferase
There are a number of different types of peptidyl transferase enzymes. Some of the most common include:
- Elongation factor G (EF-G)
- Elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu)
- Elongation factor Ts (EF-Ts)
Top FAQs
What is the primary function of peptidyl transferase?
Peptidyl transferase catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids, facilitating the elongation of polypeptide chains during protein synthesis.
Where is peptidyl transferase located within the cell?
Peptidyl transferase is located within the large subunit of the ribosome, the cellular machinery responsible for protein synthesis.
How is peptidyl transferase regulated?
Peptidyl transferase activity is regulated by various factors, including the availability of aminoacyl-tRNA substrates, the presence of antibiotics, and post-translational modifications.