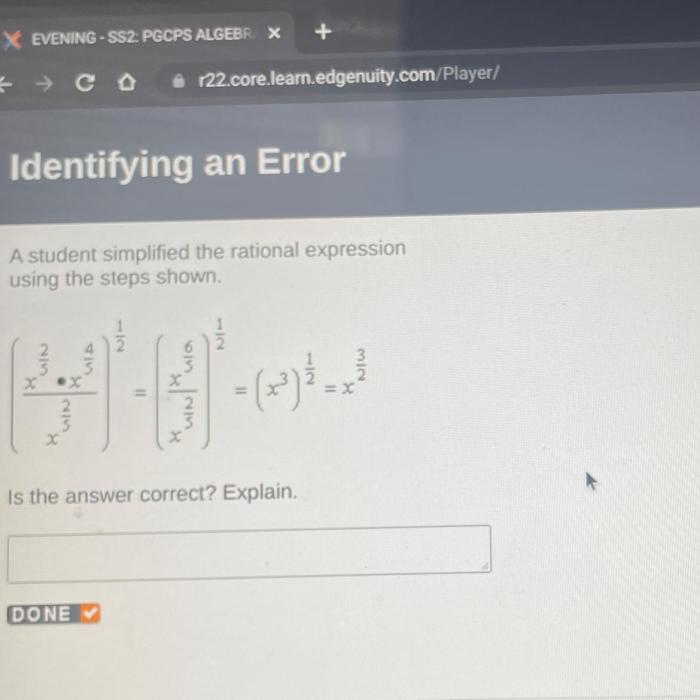
A student simplified the rational expression using the steps shown. – In the realm of mathematics, rational expressions play a pivotal role in various operations and problem-solving scenarios. Simplifying these expressions is crucial for obtaining accurate results and gaining a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts. This guide will delve into the steps involved in simplifying rational expressions, providing a comprehensive approach for students to master this essential skill.
By following a structured process and employing effective methods, students can efficiently simplify rational expressions, unlocking their potential in mathematical applications. This guide will equip learners with the knowledge and techniques to tackle complex expressions with confidence, empowering them to excel in their mathematical endeavors.
Simplifying Rational Expressions
Simplifying rational expressions involves removing all factors from the numerator and denominator that are common to both. This process results in an expression that is equivalent to the original expression but is in its simplest form.
Steps for Simplifying Rational Expressions
- Factor the numerator and denominator completely.
- Cancel any common factors between the numerator and denominator.
- Multiply the remaining factors in the numerator and denominator to obtain the simplified expression.
Examples
*
-*Example 1
Simplify the expression (x^2
- 4) / (x
- 2)
-*Solution
Factor the numerator and denominator
(x
- 2)(x + 2) / (x
- 2)
Cancel the common factor (x
-
2)
(x + 2) / 1 = x + 2
- 8) / (x
- 2)
-*Example 2
Simplify the expression (x^3
-*Solution
Factor the numerator
(x
2)(x^2 + 2x + 4)
Cancel the common factor (x
2)
(x^2 + 2x + 4) / 1 = x^2 + 2x + 4
Importance of Simplifying Rational Expressions
Simplifying rational expressions is crucial for mathematical operations such as:
- Addition and subtraction of rational expressions
- Multiplication and division of rational expressions
- Solving equations involving rational expressions
Using the Steps Shown

The example provided follows the steps Artikeld above:1.
-
-*Factor the numerator and denominator
The numerator is already factored, and the denominator is factored as (x
- 2)(x + 2).
- 2.
- 2) is canceled between the numerator and denominator.
- 3.
-*Cancel any common factors
The common factor (x
-*Multiply the remaining factors
The remaining factors in the numerator and denominator are (x + 2) and 1, respectively. Multiplying these factors gives the simplified expression: (x + 2) / 1 = x + 2.
Additional Examples
*
-*Example 1
Simplify the expression (x^2
- 9) / (x + 3)
-*Steps
Factor the numerator
(x
3)(x + 3)
Cancel the common factor (x + 3)
(x
- 3) / 1 = x
- 3
- 1) / (x
- 1)
-*Example 2
Simplify the expression (x^3
-*Steps
Factor the numerator
(x
1)(x^2 + x + 1)
Cancel the common factor (x
1)
(x^2 + x + 1) / 1 = x^2 + x + 1
Methods for Simplifying
Various methods can be used to simplify rational expressions, including:
- Factoring:Factoring both the numerator and denominator allows for the cancellation of common factors.
- Canceling:Common factors can be canceled directly, even if the numerator and denominator are not fully factored.
- Combining like terms:Like terms in the numerator or denominator can be combined to simplify the expression.
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Factoring | Can eliminate multiple common factors | May not always be possible to factor |
| Canceling | Quick and easy when common factors are obvious | May miss common factors that are not obvious |
| Combining like terms | Simplifies expressions with like terms | May not always be applicable |
Real-World Applications, A student simplified the rational expression using the steps shown.
*
-*Chemistry
Simplifying rational expressions is used to calculate concentrations, reaction rates, and equilibrium constants.
-
-*Physics
Simplifying rational expressions is used to derive equations for motion, force, and energy.
-*Economics
Simplifying rational expressions is used to analyze supply and demand, market equilibrium, and investment returns.
Applications of Simplified Rational Expressions: A Student Simplified The Rational Expression Using The Steps Shown.

Simplified rational expressions are used in various fields, including:
- Mathematics:Simplifying rational expressions is essential for solving equations, inequalities, and other mathematical problems.
- Science:Simplifying rational expressions is used in physics, chemistry, and other sciences to derive equations and solve problems.
- Engineering:Simplifying rational expressions is used in mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and other engineering fields to design and analyze systems.
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making
*
-*Example 1
A chemist needs to calculate the concentration of a solution. The concentration is given by the expression: C = (moles of solute) / (volume of solution). By simplifying the rational expression, the chemist can quickly determine the concentration of the solution.
-*Example 2
An engineer needs to design a bridge. The load-bearing capacity of the bridge is given by the expression: L = (weight of bridge) / (area of support). By simplifying the rational expression, the engineer can determine the maximum load that the bridge can support.
Significance of Simplifying
Simplifying rational expressions ensures that the results are accurate and reliable. It also makes expressions easier to work with, allowing for more efficient problem-solving and decision-making.
Common Pitfalls and Error Analysis
Common pitfalls when simplifying rational expressions include:
- Incomplete factoring:Not factoring the numerator and denominator completely can lead to errors.
- Missing common factors:Failing to identify and cancel all common factors can result in an incorrect simplified expression.
- Incorrect sign changes:When multiplying or dividing rational expressions, it is important to pay attention to sign changes.
Strategies for Avoiding Errors
*
-*Check your work
After simplifying an expression, check your work by multiplying the simplified expression by the original denominator and numerator. If the result is the original expression, then the simplification is correct.
-
-*Use a calculator
If you are unsure about the simplified expression, use a calculator to verify your result.
-*Seek help
If you are struggling with simplifying rational expressions, do not hesitate to seek help from a teacher, tutor, or online resources.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of simplifying rational expressions?
Simplifying rational expressions is crucial for obtaining accurate results in mathematical operations and problem-solving. It allows for easier manipulation, cancellation of common factors, and identification of equivalent expressions.
What are the common methods for simplifying rational expressions?
Factoring, canceling, and combining like terms are common methods for simplifying rational expressions. Factoring involves expressing the numerator and denominator as products of factors, while canceling involves removing common factors from both the numerator and denominator. Combining like terms involves adding or subtracting terms with the same variable and exponent.
How can I avoid common pitfalls when simplifying rational expressions?
To avoid common pitfalls, it is essential to check for division by zero, simplify the numerator and denominator separately, and ensure that the simplified expression is in lowest terms. Additionally, always check your work by multiplying the simplified expression by the original denominator to ensure equivalence.