Dive into the world of TC 3 22.9 board questions and gain a comprehensive understanding of their composition, components, manufacturing, applications, and design considerations. This guide will provide you with the essential knowledge and insights you need to master this topic.
From understanding the basics of TC 3 22.9 boards to exploring their diverse applications, this guide covers every aspect of these versatile boards. Whether you’re a student, engineer, or hobbyist, this guide will empower you with the knowledge you need to succeed.
TC 3 22.9 Board Basics
TC 3 22.9 boards are printed circuit boards designed to connect and power electronic components. They are typically used in telecommunications, data processing, and other electronic applications.The composition of a TC 3 22.9 board includes:
- A copper-clad laminate base
- Conductive traces
- Solder mask
- Silkscreen
The dimensions of a TC 3 22.9 board are 3.90 inches (99.06 mm) wide and 2.28 inches (57.91 mm) high.

Diagram of a TC 3 22.9 Board
The diagram shows the top and bottom layers of a TC 3 22.9 board. The top layer contains the conductive traces, while the bottom layer contains the solder mask and silkscreen.
TC 3 22.9 board questions are a valuable resource for understanding the subject matter. For further exploration, you can also refer to the unit 5 exam joshua’s law , which provides additional insights into related concepts. By utilizing these resources, you can enhance your knowledge and understanding of TC 3 22.9 board questions.
Dimensions of a TC 3 22.9 Board
The dimensions of a TC 3 22.9 board are 3.90 inches (99.06 mm) wide and 2.28 inches (57.91 mm) high. These dimensions are standardized by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA).
TC 3 22.9 Board Components
The TC 3 22.9 board is an essential component of the aircraft’s electrical system. It serves as a central hub for various electrical functions, including power distribution, switching, and protection.
The board is composed of numerous components, each performing a specific function. These components can be broadly categorized into several types:
Power Distribution Components
- Main Power Bus: The main power bus is the primary conductor that distributes electrical power throughout the aircraft. It receives power from the generators and distributes it to various subsystems.
- Secondary Power Buses: Secondary power buses are connected to the main power bus and distribute power to specific areas of the aircraft, such as the cockpit, avionics, and lighting.
- Circuit Breakers: Circuit breakers are protective devices that interrupt the flow of electrical current when it exceeds a predetermined level, preventing damage to the electrical system.
Switching Components
- Relays: Relays are electromechanical devices that use a small electrical current to control a larger electrical current. They are used to switch electrical circuits on or off.
- Contactors: Contactors are similar to relays but handle higher electrical currents. They are used to control high-power loads, such as motors and generators.
Protection Components
- Fuses: Fuses are sacrificial devices that break the electrical circuit when the current exceeds a predetermined level, protecting the electrical system from damage.
- Surge Suppressors: Surge suppressors protect the electrical system from voltage spikes and transients, which can damage sensitive electronic components.
Monitoring and Control Components
- Voltmeters: Voltmeters measure the electrical potential difference between two points in the electrical system.
- Ammeters: Ammeters measure the electrical current flowing through a circuit.
- Control Switches: Control switches are used to manually control the electrical system, such as turning on or off lights or avionics.
TC 3 22.9 Board Manufacturing
The manufacturing of TC 3 22.9 boards involves the use of specialized materials and a carefully controlled process. The materials used include high-quality copper for the conductors, a non-conductive substrate material such as fiberglass or ceramic, and a protective solder mask.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of TC 3 22.9 boards typically follows a series of steps:
- Substrate Preparation:The substrate material is cleaned and prepared to receive the copper traces.
- Copper Deposition:Copper is deposited onto the substrate using a process called electroplating.
- Etching:The copper is etched away to create the desired circuit pattern.
- Solder Mask Application:A solder mask is applied to protect the copper traces from oxidation and shorts.
- Soldering:Components are soldered onto the board.
- Testing:The board is tested to ensure it meets specifications.
The manufacturing process is closely controlled to ensure the quality and reliability of the boards.
Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates the manufacturing process of TC 3 22.9 boards:
[Flowchart: Manufacturing Process of TC 3 22.9 Boards]
The flowchart provides a visual representation of the steps involved in the manufacturing process, highlighting the key stages and the flow of materials and components.
TC 3 22.9 Board Applications: Tc 3 22.9 Board Questions
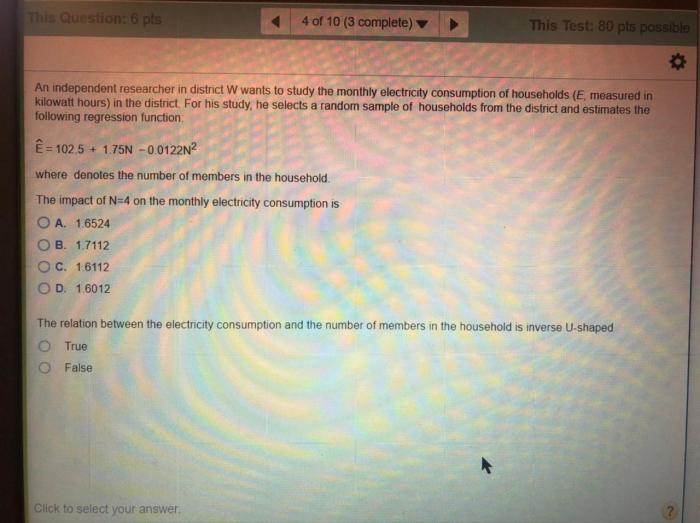
TC 3 22.9 boards find widespread use in various industries and applications. Their versatility and ability to handle high currents and voltages make them suitable for demanding electronic systems.
Here are some real-world examples of TC 3 22.9 board applications:
Industrial Automation
- Control systems for machinery, robots, and production lines
- Monitoring and data acquisition in manufacturing processes
Power Distribution and Control, Tc 3 22.9 board questions
- Distribution boards in electrical substations and power plants
- Control panels for industrial equipment and motors
Renewable Energy Systems
- Solar photovoltaic systems
- Wind turbine controllers
Transportation
- Electrical systems in electric and hybrid vehicles
- Control panels in trains and subways
Medical Equipment
- Patient monitoring systems
- Medical imaging equipment
TC 3 22.9 Board Design Considerations
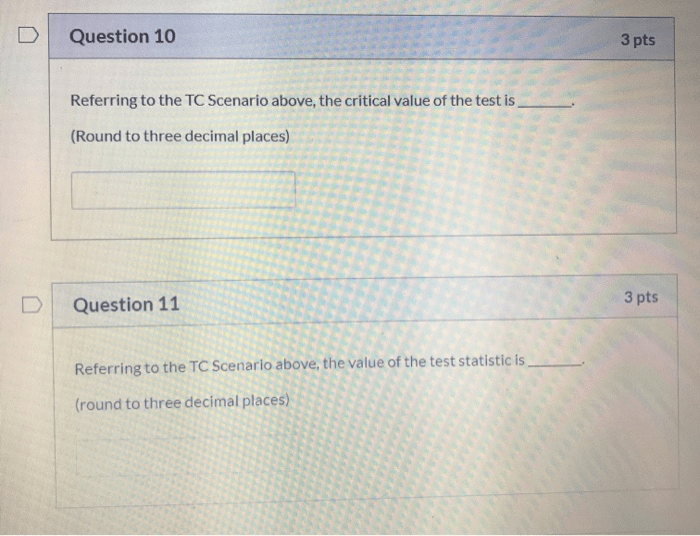
Designing TC 3 22.9 boards requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure optimal performance and reliability. These factors include:
Material Selection
- Consider the electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties of different materials.
- Evaluate the cost, availability, and manufacturability of each material.
Circuit Layout
- Optimize trace routing to minimize noise and crosstalk.
- Ensure proper spacing between components to prevent short circuits.
Power Distribution
- Design the power distribution network to handle the current requirements of the board.
- Use decoupling capacitors to minimize voltage fluctuations.
Thermal Management
- Consider the heat dissipation of components and design the board to facilitate heat transfer.
- Use heat sinks or other cooling methods to prevent overheating.
Signal Integrity
- Control impedance and minimize reflections on signal traces.
- Use proper termination techniques to prevent signal distortion.
Manufacturability
- Design the board with considerations for automated assembly and testing.
- Follow industry standards and guidelines to ensure compatibility with manufacturing processes.
Checklist of Design Considerations:
- Material selection
- Circuit layout
- Power distribution
- Thermal management
- Signal integrity
- Manufacturability
- Cost and availability
- Reliability and performance
- Environmental considerations
Best Practices for TC 3 22.9 Board Design:
- Use high-quality materials and components.
- Follow industry standards and guidelines.
- Perform simulations and testing to validate the design.
- Consider the long-term reliability and performance of the board.
FAQs
What are the dimensions of a TC 3 22.9 board?
TC 3 22.9 boards typically have dimensions of 100mm x 160mm.
What materials are used to manufacture TC 3 22.9 boards?
TC 3 22.9 boards are typically made from high-quality FR4 material, which provides excellent electrical and mechanical properties.
What are some common applications of TC 3 22.9 boards?
TC 3 22.9 boards are used in a wide range of applications, including industrial control, medical devices, and consumer electronics.